- Prevailing trade tensions and currency volatility identified as major challenges to RMB internationalisation
- Use of RMB in cross-border investment and trade settlements is growing
- Liberalisation of China’s financial markets, trade facilitation arrangements and PBOC digital currency will increase RMB usage
Despite headwinds from the ongoing trade tensions and unprecedented disruption caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, businesses globally are still increasing their use of renminbi (RMB) in international transactions.
Supporting the continued internationalisation of the RMB are the initiatives to liberalise China’s financial market, Beijing’s trade facilitation arrangements with key partners and the People’s Bank of China’s (PBOC) launch of digital currency.
These are the key highlights of the RMB Internationalisation Report 2020 published by China Construction Bank in partnership with The Asian Banker based on a corporate survey that evaluates the progress in the internationalisation of the currency and developments in cross-border RMB-denominated products and businesses. The survey involved 643 executives from three groups of institutions, comprising companies and enterprises based in China (Chinese companies),companies and enterprises based outside of China (overseas companies) and financial institutions (FIs) around the globe.
Although concerns over trade frictions and COVID-19 pandemic remain, respondents surveyed were generally optimistic about the internationalisation of the RMB in 2020.
New regulations and frameworks introduced by various Chinese agencies in 2019 provided greater impetus to RMB internationalisation. The introduction of new Free Trade Zones, expansion of the Belt and Road Initiative and inclusion of China “A” shares in the MSCI index are among key elements contributing to the increased use of RMB globally.
To attain international currency status, the current path of opening up of financial markets must be maintained to facilitate the greater use of RMB across the world while enhancing the interconnectivity and integration of both on-shore and off-shore market infrastructure.
The RMB proved to be remarkably stable and resilient amid adverse and uncertain economic conditions in 2019 and 2020 is expected to see the introduction of more robust internationalisation measures to shore up and strengthen the currency.
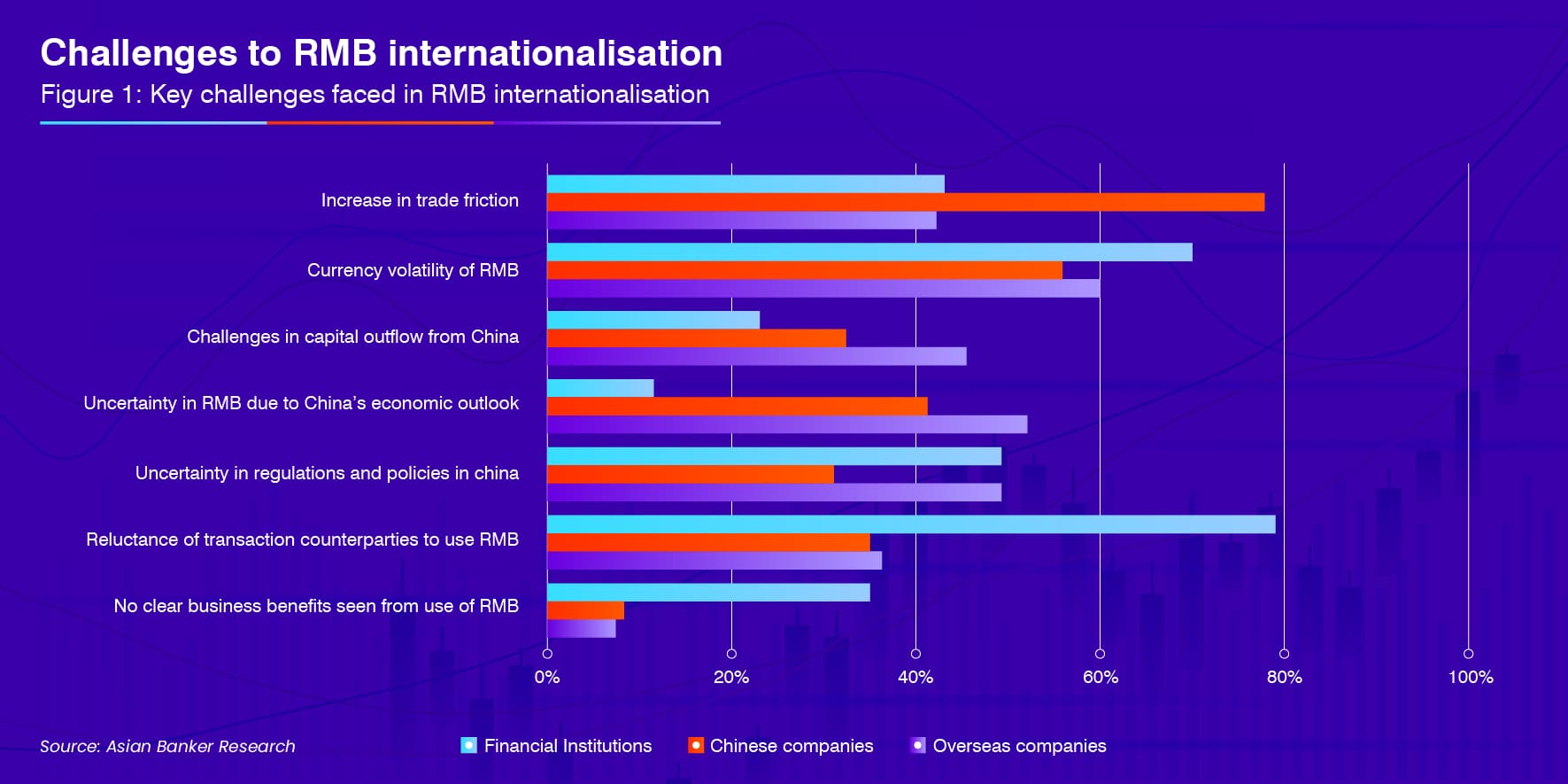
Challenges to RMB internationalisation
Trade tensions between the United States and China remained the most significant concern, 74% of Chinese and 62% of overseas companies indicated that they had affected their usage of RMB for international transactions in 2019. Other potential challenges for respondents included currency volatility, with 67% of financial institutions rating it as a top challenge.
To mitigate the risk, a significant proportion of respondents,57% of overseas companies and 44% of Chinese companies, hedged their currency risk exposure, indicating a more mature foreign exchange market for RMB and increasing awareness of participants to manage currency volatility risk.
Source:Asian Banker Research
The COVID-19 pandemic presents unprecedented disruptions to the global economy and world trade, with the International Monetary Fund predicting global economy to shrink 3% this year and $9 trillion over two years.
With market participants seeking a “flight to safety”, there will be a rising demand for safe assets. Notwithstanding the rise of the dollar, the RMB is well positioned to capitalise on the expected return to normalcy of business activities in China as a result of effective pandemic mitigation and economic stimulus measures taken by the government.
Given that market optimism in China is returning gradually, the RMB has stabilised compared with other major global currencies that are seeing significant drops in value. For international market participants this is reflected in less foreign exchange volatility marking RMB-denominated investments as the preferred asset class and currency in settling cross-border payments. Resumed business activity will also bolster support in the RMB as business confidence is restored.
Use of RMB in trade and investment is growing
Among overseas companies, 44% increased exports to China in 2019, up from 33% in 2018., For 2020, 40% of respondents planned to increase exports to China.
Among all RMB products and services, cross-border trade settlement witnessed the highest increase in use by companies in 2019. Consistent with the trend seen in 2018, more than half the companies surveyed,65% of overseas and 51% of Chinese companies and 67% of FIs increased trade settlement using RMB in 2019, while only 16% of Chinese and 12% of overseas companies and 11% of FIs reduced their usage. The growth is expected to continue in 2020, with 78% of FIs, 59% of Chinese companies and 51% of overseas companies planned to increase their cross-border trade settlement using RMB.
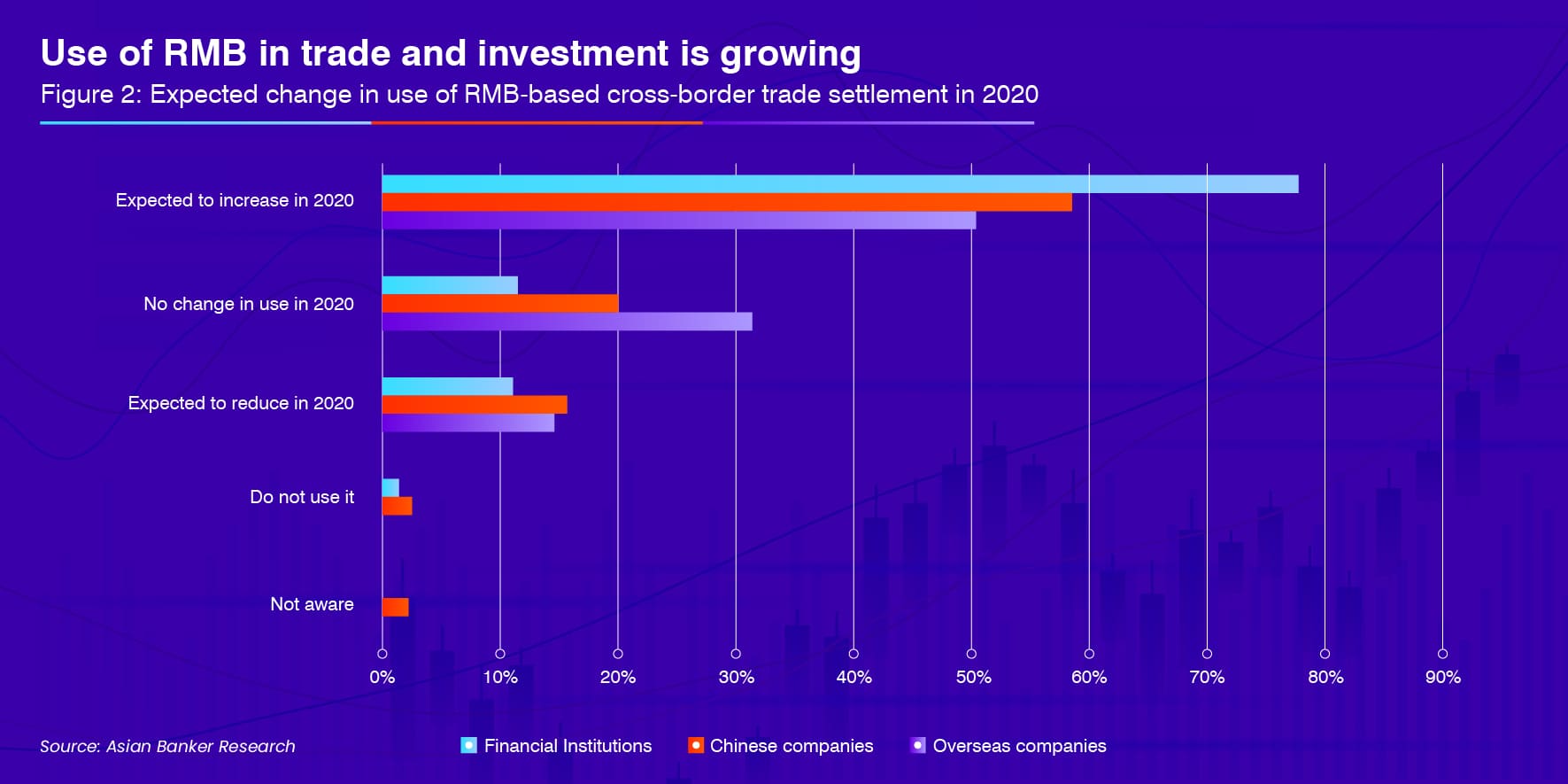
Among companies, 50% of overseas and 26% of Chinese respondents increased their use of RMB in cross-border direct investments, while 37% of overseas companies and 30% of Chinese companies maintained the status quo in 2019. The trend is expected to continue in 2020 as 50% of overseas and 38% of Chinese companies as well as 78% of FIs expected to increase their cross-border investments in RMB in 2020.
Forty-four percent of overseas and 36% of Chinese companies increased their RMB holdings outside China, while only 13% of overseas and 20% of Chinese companies reduced their holdings. This trend is also indicative of growing RMB holdings in line with other products. Among FIs, 44% increased their RMB holdings while 11% commented that they did not engage in it.
Going forward, the trend is likely to accelerate as 40% of Chinese companies and 38% of overseas companies indicated that they will increase their RMB holdings outside China in 2020. Among FIs, more than half either expected to increase or retain the same level of RMB-based holdings outside China.
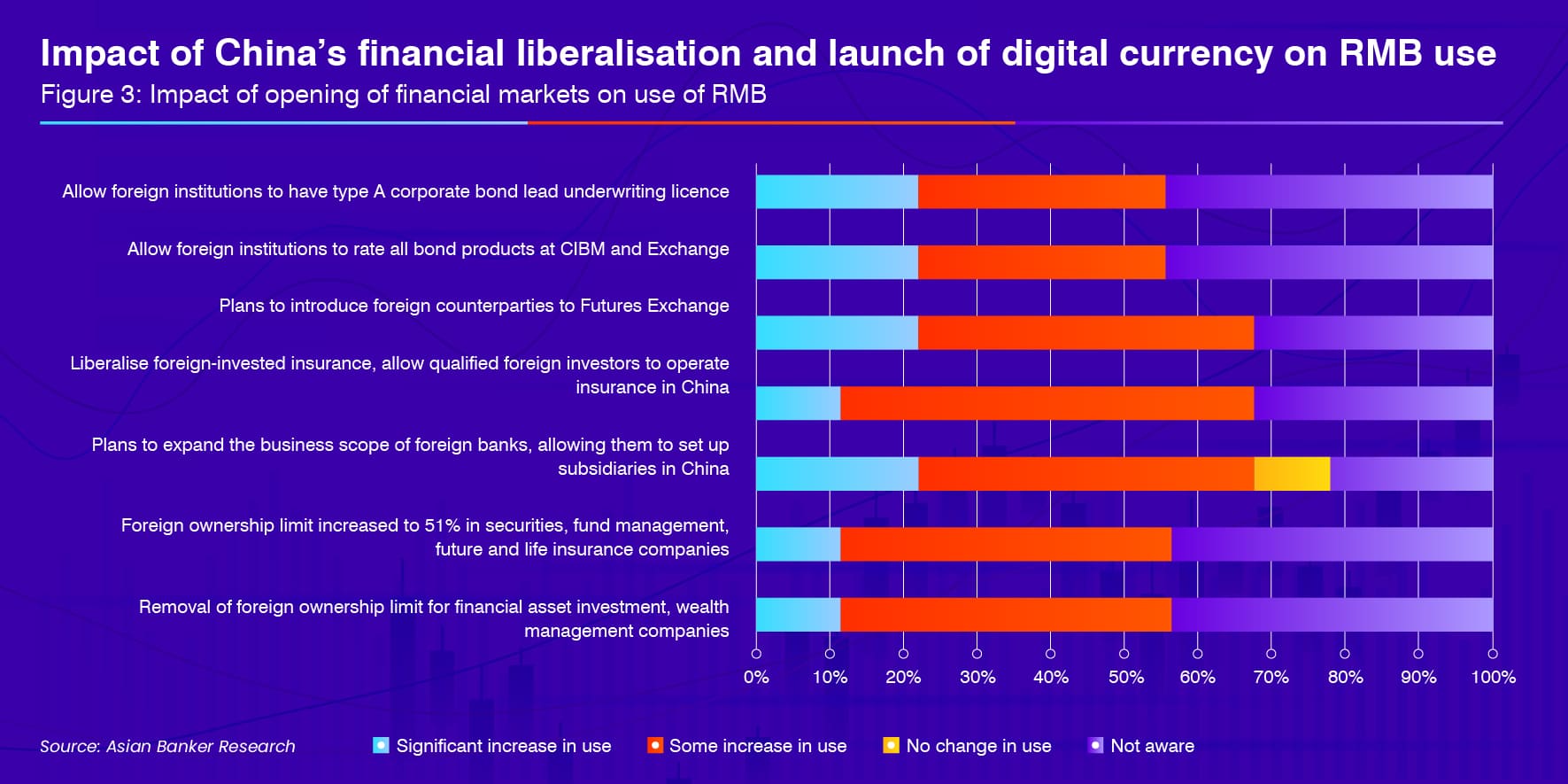
FIs were asked about the likely impact of the opening of financial markets on them and 29% said they expected this to boost the usage of RMB as a financing currency, while 25% of respondents expected these measures to enhance access by foreign financial institutions to China’s financial sector. Twenty-two percent and 12% also expected more investment into China’s bond market and stock market, respectively, following further liberalisation.
The potential launch of a central bank digital currency in conjunction with further financial market reforms will complement efforts to steadily internationalise the RMB. With the underlying technology and regulatory framework underpinning the basic functions of a digital currency encompassing circulation, payment, issuance and anti-money laundering largely in place or being finalised, the imminent launch of a national digital currency is in progress.
The survey revealed that 67% of FIs had a positive view to a national digital currency being issued by the PBOC, and this favourable sentiment resonated strongly with 57% of overseas and 55% of Chinese companies.
On using the digital currency, 52% of overseas companies and 44% of FIs were willing to use it once all institutional frameworks governing the currency are in place, more proactive than 27% of Chinese companies that felt the same.

































