In the latest Asian Banker annual survey of cash management trends across Asia-Pacific, focus on meeting automation needs of corporate treasury and demand for bank agnostic channels supporting wider industry-standard formats emerged as key themes. Uncertainty around trade flows, rates normalisation, regulation and new technology innovations have increased demand for more visibility into global liquidity, enhanced workflows and control internally, as corporates look for simplified connectivity to balance cost and financial risks.
Corporate concerns have also mounted on maintaining day-to-day liquidity as enterprises spend considerable efforts on short-term cash-flow forecasting. In ensuring the adequacy of funds in operating accounts, the dynamic role of corporate treasury has thus transformed from basic cash management to more complex and centralised treasury functions. Solutions targeted at cash concentration, sweeping, and pooling make best use of internal liquidity, whilst minimising reliance on external borrowing. However, as Asian corporates expand globally and extend their business and customer networks, treasury management is bound to gain complexity.
This has driven banks to build solutions, specifically catering to a cross-border and cash light transaction economy. From leveraging machine learning for cash-flow forecasting to minimising idle float, or optimising account structures for adequate cash positioning, banks identified quickto-market and tailored solutions and industry standards built on harmonised communication as critical cash management needs
Automation of treasury function and achieving operational efficiency through common industry standards are top priorities amongst banks
Figure 1. Emerging Key Themes in Cash Management 2019/2020 based on % of banks identifying them as important
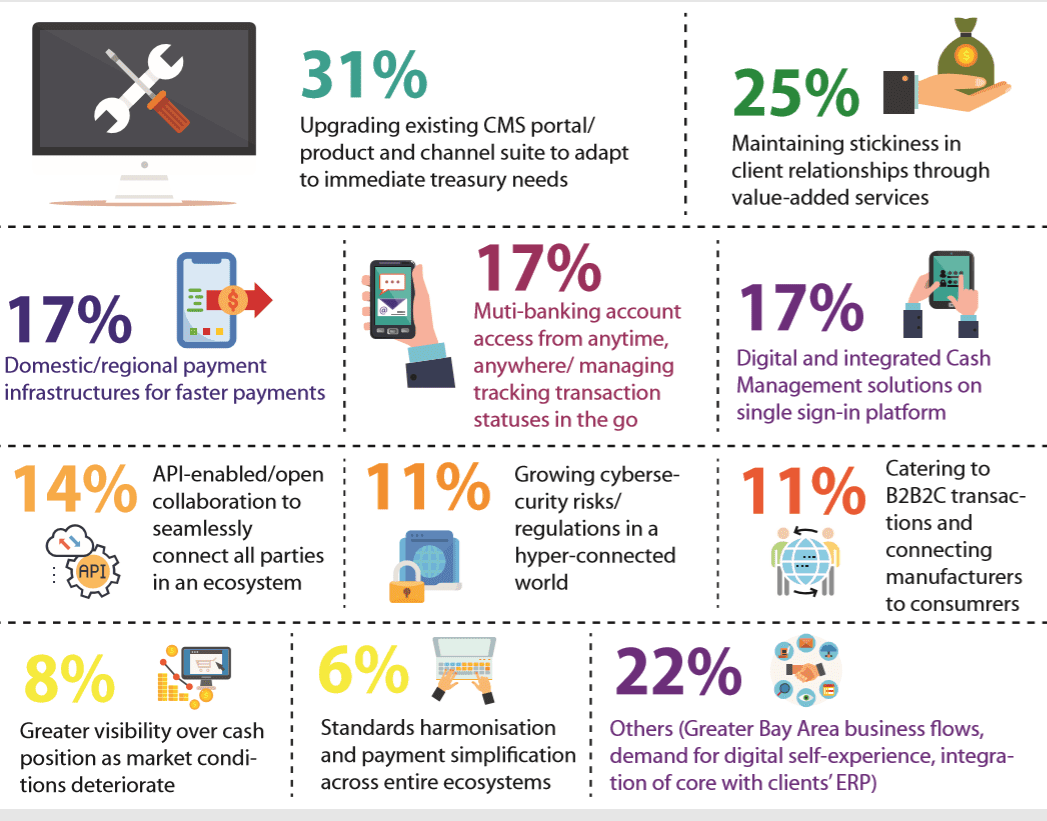
Meeting immediate treasury needs through new market infrastructures
Treasury centres are looking at their banks to move beyond end-of-day balance and transaction reporting to providing more value-added and real-time services. The impetus for meaningful, focused and actionable input is essential as the treasury continues to assume a broader, more strategic role to support increased business flows with fewer resources. More and more corporates are integrating instant payment schemes to benefit from increased visibility over funds, as well as certainty and finality of payment transaction. In response to ever-changing needs, several banks are now live on real-time payment
system and are looking to strengthen efficiency by consolidating many products – each with its infrastructure, user entitlements, and security protocols – to help treasuries with their processes.
Bank of China (Hong Kong) observed a growing trend of consumers turning to mobile payments, especially on third-party payment platforms such as Alipay and WeChat Pay. In response to this, Bank of China (Hong Kong) leveraged the Faster Payment System and provided Merchant Presented QR Code Solution for consumers to have greater visibility and control over their cash position.
With the launch of India’s new Unified Payments Interface, Kotak Mahindra Bank improvised its existing product suite to enhance transparency with real-time updates. New products reduce the idle float while investing them in high return instruments to help manage the cash cycle in a very efficient way. The bank additionally created a pooling structure to move funds to high interest products, which further enhances revenue for the clients. Yes Bank identified corporates increasing demand for a digital self-service experience. It propelled the use of Application Programming Interface (API) technology to enhance the collection and validation process and migrate more clients into straightthrough reconciliation (STR) through web services integration. Singapore based banks are aggressively extending help to corporates to manage their transition to a cashless ecosystem. United Overseas Bank is supporting the industry initiative to go paperless by reducing cash and chequebased transactions. In response to the launch of PayNow Corporate, it deployed API services to add value to clients’ end-to-end process chain, enhancing payment and collection efficiencies, whilst reducing payment risk across channels. OCBC Bank, on the other hand, partnered with fintech companies to deliver customised industry solutions through its first-to-market transactional API solutions.
In Vietnam, as public services become more digital, transaction banks are heavily investing in new payments and cash management system to better serve the core cash management needs. Vietcombank launched an automated web channel with a secure interface to promote electronic solutions, which meets the needs of clients in infrastructure, healthcare and energy sectors. Techcombank stressed on the need of rationalising accounts and offsetting rising operational costs amid pressure from regulatory tightening. It delivered solutions for large corporate clients through increased automation with its cash transaction analysis tools.
According to the German-based lender Deutsche Bank, complete oversight of liquidity positions ensures that corporate treasurers can better optimise working capital through rebalancing towards internal financing sources and are better able to make strategic treasury decisions. The bank leverages in-house capabilities, APIs and extensive fintech/industry partnerships to provide multi-tier client service model, including self-service such as cash inquiry, dedicated client service officers and SWIFT inquiries at its operations hubs.
Multiple standards and the increasing need for interoperability of information
Different messaging standards are an obstacle to data automation capabilities, with payments often having to be converted at payment gateways and the subsequent transaction data being either misreported or lost. Separately, for banks and financial institutions, it is a significant impediment to fulfilling anti-money laundering compliance and fraud regulatory reporting.
As connectivity challenges grow more significant with regional corporates expanding globally, software vendors and banks have launched many formats for how these transactions are encoded. The decision by major central banks and SWIFT to migrate to ISO 20022 messaging standard promises greater interoperability between various settlement networks, leading to clear communication, richer data flows, improved levels of STP and a less headache to meet regulatory compliance. Institutions are thereby laying foundations for industrial-strength connectivity. They identified bank agnostic connectivity and integrated payments processing platform as crucial best practices to improve efficiency and better serve clients.
For Malaysian corporates, there is a need to access multi-banking accounts from ‘anytime’ and ‘anywhere’. This led the RHB Bank to deliver an integrated regional cash management platform to enable the clients to view and manage their overseas accounts in a single platform.
Sri-Lankan domiciled Hatton National Bank stressed on the importance of multi-bank and immediat payment processing to the beneficiaries maintaining accounts at other banks. Leveraging its strong network and digital alternate channels, it caters to bulk processing of real-time Interbank Payments. To drive flexibility to adapt to customers’ existing legacy formats and processes, Yes Bank adopted configurable systems that deliver end-to-end enterprise resource planning (ERP) integration between its customers, banks and clearing houses.
Demand for total solutions incorporating standardised modules for collection and payments, corporate and trade finance has grown in Taiwan. Considering the diversity of clients, Cathay United Bank developed the multinational enterprise web version for SME/micro-enterprises. It also launched WeChat banking services to maximise the value of multiple platforms with the minimum resources of a single platform.
For corporates to achieve Host-toHost connectivity with their central cash bank, Deutsche Bank drives bank agnostic-connectivity via SWIFT. With an increasing trend to switch to electronic treasury workflow, corporates are further optimising processes with their multiple banking partners by utilising ISO 20022 XML v3 files, which are primarily standardised across banks. The bank is in the process of rolling out Galileo, a new single payment processing platform, that integrates the complete set of payment types including low value, high value, bulk, XML, SWIFT gpi and instant payments.
Upcoming regulations like BASEL III have prompted the banks to plan the required regulatory changes way ahead of implementation. New standards under BASEL III redefine the global standards of deposits and the way they look and work through their balance sheets. On top of this, new market infrastructures that have warmed up to emerging technologies such as meeting 24/7 payment requirements, are radically changing flow management. With the emergence of next-generation cash management solutions, the pressure on corporate treasury is now to enhance their bottom-line performances.

































